Industry Talk
Regular Industry Development Updates, Opinions and Talking Points relating to Manufacturing, the Supply Chain and Logistics.Getting Immersed in Supply Chain Management

Perspective
As we see seeds sown grow into a plant and subsequently transform to a fruit yielding tree, similarly the seeds of the emerging Digital technologies, such as mobility/GPS, Cognitive analytics/AI/BI, additive manufacturing/3D printing, cloud technology and pervasive computing, have now pushed the business into the a new wave of automation and integration. The success for these forces can be attributed to completely new ways of doing the same business, innovation being given priority and penchant to remain competitive while providing enhanced value to customers.
We believe that Business 4.0 is the next big thing in ways of conducting business. An integral element of Business 4.0 is the immersive technology which coalesces physical reality with digital space. Through interactions between the real and virtual worlds through IoT, the first benefit available is the shortening of the value chain in terms of lead times and response times. This means being next to the customers, adapting to changing market situations, faster value realization and staying business relevant. Leading companies must adopt immersive technology as soon as possible to remain competitive, business relevant, improve operational efficiency, gain financial benefits, reduce wastage and enhance skills. According to a recent estimate by Goldman Sachs, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are expected to grow into a $95 billion market by 2025. (https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2017/09/augmented-and-virtual-reality-will-change-how-we-create-and-consume-and-bring-new-risks/) Gartner predicts that the adoption rate will pick up moderately by 2020 with business adopting more than the customers (https://www.gartner.com/smarterwithgartner/exploring-augmented-reality-for-business-and-consumers/). Gartner also mentions “We predict by 2019, AR, VR and Mixed Reality (MR) solutions will be evaluated and adopted in 20% of large-enterprise businesses.”” (https://www.gartner.com/smarterwithgartner/transform-business-outcomes-with-immersive-technology/) Interested customers must explore the risks associated and analyze the supply chain readiness before embracing this technology. We are working with companies and partners in ensuring smooth landing of VR and AR into their operations by blue printing the supply chain, finding potential gaps, recommending the most optimal VR/AR solution and then conducting the change management process post implementation.
Need for VR, AR in Supply Chain
More than that, their customers are more demanding in terms of product innovation, speed to serve, cost to serve etc. In order to respond swiftly to customer requirements and managing a vast number of orders around an ever bulging product portfolio, the value chain needs to accelerate response with agility and flexibility. VR, AR and MR allow faster product development through real-time interactions of co-located teams. On time delivery is a KPI for which such giants invest to the limit to be able to satisfy customers. AR can be helpful through Smart glasses, Head Mounted Displays and RFID. Diagnostic and analytics techniques to monitor health of supply chain are a regular feature in such industries to tackle any issue on an immediate basis. Immersive technologies allow setting up of proxy supply chains (Digital Twin, through simulation techniques) right on the desktop to address any evident supply chain problem. Large companies like DHL, Ikea have already implemented immersive technologies in their supply chains. To ensure quality and compliance, supplier governance is now very critical and companies can conduct virtual meetings and tours to audit suppliers conveniently.
Types of Immersive Technologies
VR is simulating the near term reality for a user to experience. The applications of VR include arcade gaming, location tracking, flight simulation, military training purposes, medical treatments, entertainment through telepresence, pervasive gaming, digital twin etc.
AR is an extension or improvement to VR. More than just providing display, AR helps the user to “touch and feel” the virtual information provided over the reality realm at real time speed. The technology enabling AR includes accelerometers, smartphones, smart glasses, head-mounted displays (HMD), virtual tables etc. also called holographic devices.
MR is creation of new environments by using real world objects and virtual objects. MR is capped on one side by physical reality and on the other by digital reality with VR and AR in between.
Benefits of Immersive Technologies in Supply Chain
Ranging from enriched customer experiences, S&OP meetings, prototyping, warehouse operations to logistics – supply chain automation can be boosted by use of immersive technologies.
Starting from the customers’ side, there is huge potential to be exploited in terms of providing virtual tours of stores across the world in order to offer a variety of products. Especially in industries with shorter product lifecycles like fashion and retail, customers can virtually try on apparel and decide what to buy. This reduces physical inventory and returns and pushes sales up. Customers also get the unique shopping experience.
Today the S&OP cycles have become shorter, more frequent and definitely dynamic. Holding virtual meetings to plan a quick response to any external market pulse is important to stay competitive where executives participate more than just through a video conference.
Virtual prototyping allows to preview rapid iterations, testing and conduct failure mode effects analysis before actualization thereby reducing costs.
AR allows more automated operations with less manual effort. For example, while receiving a pick list, the process of order fulfilment can be initiated through a smart glasses, followed by the most optimal route selection to pick the products and ultimately place each picked product.
In delivery operations, retrieving the right product is expedited through use of such headsets or glasses which locate the product based on the geo position of the deliverer and the delivery address. Further, drivers need not carry physical lists leading to higher productivity.
On the other side, personnel training can be conducted from anywhere in the world through virtual classrooms. Governance of the factories can be done remotely and 24×7 by managing staff duties (based on time zone and geography) accordingly through use of such devices. Product failure analysis can be conducted through VR and AR devices allowing simulation testing where running multiple scenarios on a prototype before finalizing a design for launch has been made possible.
Challenges to be addressed before rolling out Immersive Technology
Certain challenges are always hovering with any nascent technology. In this case, infrastructural problems like poor speed connectivity, hardware availability, compatibility issues, application ecosystem version etc. are to be addressed before implementation. Another impediment in the swifter pick-up is the steep hardware cost involved. With business sensitive information being scanned through such VR, AR devices, the cybersecurity levels are required to be raised involving parallel compatible security software deployment. Employees trained on orthodox / conventional operating methods, might offer resistance arising due to prolonged wear ability, additional gears to be handled etc. which needs to be calmed down through proper orientation and training. Before an implementation, proper onboarding of all stakeholders is essential to reduce friction, complete requirements gathering, faster design thinking and thorough solution building.
Among these, hardware availability and costs are the first deterrents to adoption. Firstly, lack of talented content developers promotes poor integration of audio and visuals to provide a virtual experience. This makes the user view a stitched environment with “seams and stitches” rather than homogeneity. Being new, the mid-range VR and AR devices like accelerometers, smartphones, smart glasses, head-mounted displays (HMD) cost around $350-500 per device and if we add the cost of controllers and allied set-ups like cameras, lights etc. the overall cost can rise drastically. The features of a VR headset undergo rejuvenation every six months and the performance usually decreases in less than a year. With a few prominent manufacturers, the hardware available is still not mature enough.
The neural network at most large organizations is an integrated ERP which controls all major functions. In order to make use of these AR, VR devices more pronounced, they must be able to talk to ERP systems on real-time basis. It is still under exploratory phase where such integrations are being studied by giants like SAP, Oracle with Google Smart Glasses.
Basic infrastructural issues like poor speed and cybersecurity need to be addressed through network overhauls and firewalling as a pre-requisite.
Solution Framework
A solution framework is necessary to navigate the implementation of immersive technology. In our experience we have developed a transformational approach to deliver quick wins and incremental value while simultaneously performing continuous improvement.
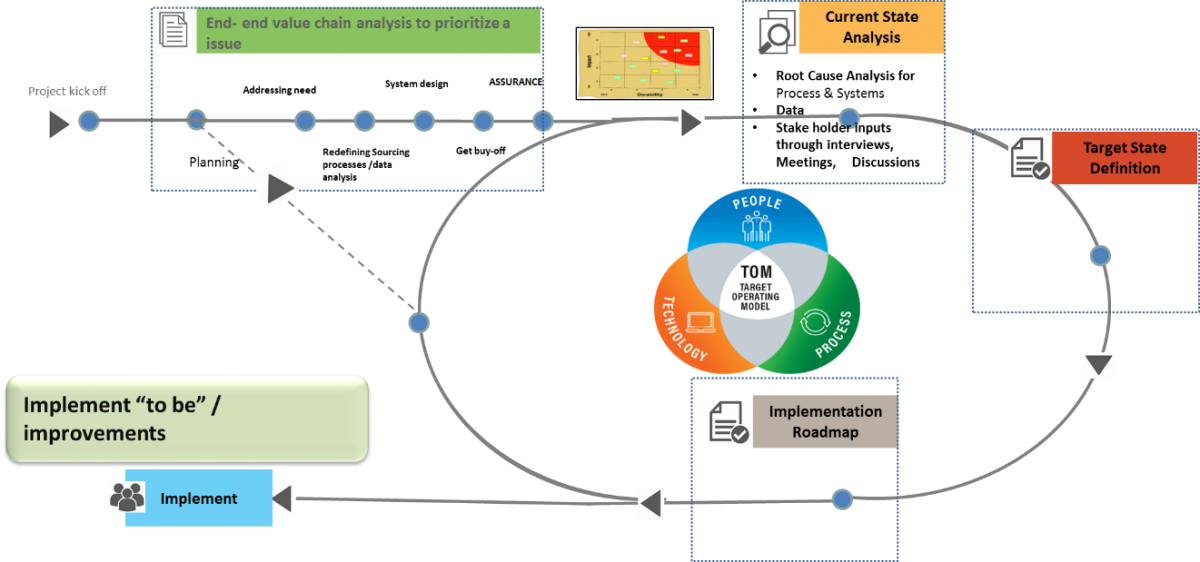
Immersive Technology Transformation Solution Framework (ILLUSTRATIVE)
There is a lot of talk about upskilling, learning, quality assurance, talent development etc. when it comes to counting keys to success. With business spread across geographies and cultures, a very important aspect is training and sensitizing the personnel with the latest techniques, quality conformities, and governance policies. Using the lean framework, we can map the end-to-end process highlighting the nodes where intervention is needed in terms of training, guiding, mentoring, inspecting etc. Let’s talk about each aspect separately. When it comes to training, we will assess the existing capabilities of the manpower, machines and processes.
By prioritizing the gaps, we can propose technological improvements in terms of smart e-classrooms with compatible equipment like head mounted displays, virtual screens, smart glasses and location tracking for personnel to participate in training sessions conducted from remote centers. Quality has become the deal breaker and if not paid proper attention can lead to shutting down of businesses. Hence for quality inspection, we suggest a solution where the quality check points are analyzed, detailed out and understood along with the business users. Then at quality critical points, we propose to implement use of suitable AR apps for smart phones which is a cost effective way to determine the quality issues like cracks, defects, failure points etc. and provide online troubleshooting from R&D centers located far away from manufacturing plants.
Immersive Technologies in Supply Chain Today
- DHL has Vision Picking Programming which allows use of advanced smart glasses to boost efficiency and minimize the errors in the picking and packing operations. Ubimax provided the software xPick and Glass Enterprise Edition and Vuzix M100 and M300 hardware was used.
- Ikea has released a VR and AR application which allows shoppers to view how a particular product will fit-in to their house on a virtual platform
- Skype on Microsoft HoloLens allows virtual meetings
- Microsoft HoloLens is the leading MR device which allows users to walk around tourist locations across the world and can be also be utilized for virtual store walk through too for retail customers
- Google Glass smart glasses is an optical mounted head display which can be used for warehouse operations automation.
Call to Action / Recap
VR is touted to have a 50% adoption rate and close to 23% adoption rate in the next 3 years. AR is 67% favored among the corporates with 30% committing in the next 3 years. (https://www.xcubelabs.com/our-blog/immersive-technology-bringing-vrar-manufacturing/) Total revenue for virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) is projected to increase from $6.1 billion in 2016 to over $215 billion in 2021. Such technologies need to be adopted swiftly in order to harness the first movers’ advantage.
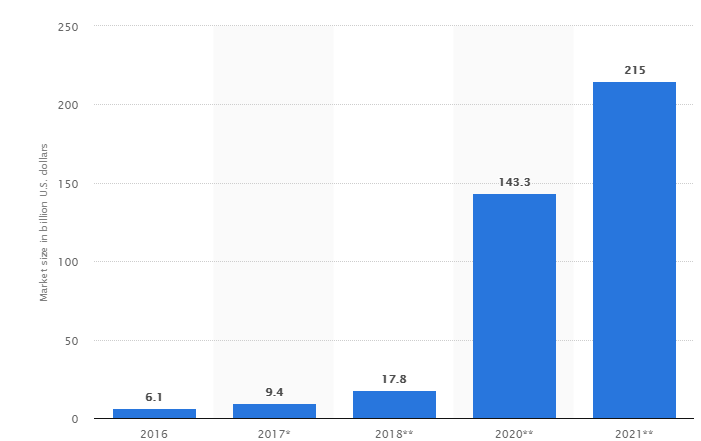
(https://www.statista.com/statistics/591181/global-augmented-virtual-reality-market-size/)
These technologies are not going to radically change the business but will gradually become seamlessly joined to the day-to-day operations. Operations will need to absorb VR, AR and MR to improve performance and accuracy. Enterprises aiming to be ahead in the game must learn, absorb, train on and execute immersive technologies.