Retail
Retail supply chain software for enhanced supply chain efficiency, encompassing warehouse & transportation solutions, inventory control, and strategic/planning modules.Optimizing Store Delivery Windows at One of the World’s Largest Retail Chains

Introduction: Individual stores at this retailer were experiencing a 15-hour delivery window for groceries. The 15-hour delivery window creates several challenges eroding productivity and profitability. Random trailer arrival times to drop product for the store creates staffing uncertainties and/or labor waste and inefficiencies. A significantly shorter delivery window (4 hours) was proposed for stores to save on staffing by improving the utilization of store associates. This strategy has become increasingly important for the retailer as it pushes to improve productivity and same store sales and profitability.
Overview of the process:
1) Order Drops
- The store orders that need to be processed the next day drop into the DC. These would include (backlog orders) orders that were not processed the previous days.
- DC Operations
- Items are picked from the DC shelves to satisfy the store orders.
- The store orders may be picked from the shelves at different times of the day depending on the day of the week and how the orders dropped into the DC.
- These picked orders are loaded onto the trucks to be delivered to the stores.
2) Transportation Planning (after order drops)
- The routing software receives the store orders including quantity ordered and due dates.
- The software develops the sequence of store drops using a solver that optimizes based on a set of transportation objectives viz a viz miles travelled subject to constraints (capacity constraints).
- Output is the sequence of stops/drops on a route.
3) Transportation Execution
- The routes generated are tendered to the carriers.
- These routes are not static. Routes with different sequences of stops are generated for different days.
- Weather conditions, local traffic patterns, congestion due to accidents are some of the conditions considered that could affect transportation times.
4) Store Processing
- The orders are received and processed at the store.
Challenges in the Current Process:
- The workload at the DC is unbalanced during the day with high peaks (lots of activity) at certain times and not much activity during other times of the day (Figure 1). This leads to inefficiencies in labor/staffing planning at the DC.
- The routes generated during the execution phase are not static and vary by day to day. This leads to execution problems in the routing process. External conditions that could affect transportation times: weather conditions, local traffic patterns, congestion due to accidents, etc. separately and collectively play a role in exacerbating these execution problems.
- It is very difficult to provide the stores a time definite 4-hour window within which they can expect their orders. As a result this leads to stores having to anticipate and plan for deliveries at any time during the day.
Figure 1: Unbalanced Workload at DC (Ungrouped Stores)
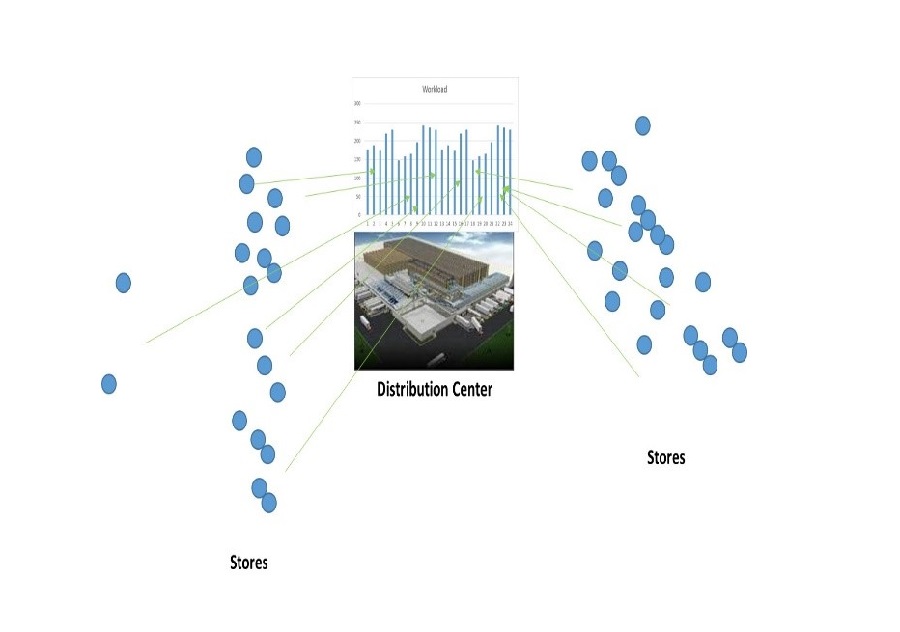
Figure 2: Balanced Workload at DC (Grouped Stores)
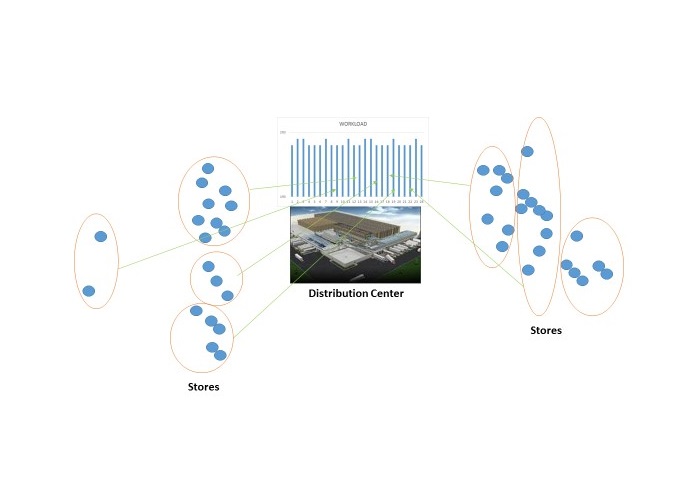
Solution Approach: The distribution center supplies product to stores. These stores are located at different distances from the DC and have different time and volume requirements. Depending on the product shipped, volume can be stated in pounds, cubes or cases. Using a clustering algorithm, stores are grouped together by distance, time and volume requirements so that the volume needs of the stores in a group can fill a truck to its maximum capacity. This grouping guides the sequence of store order fulfillment at the DC (Figure 2).
The solution proposed generates optimized 4-hour delivery window for each store aligned to the given grocery DC based on the input parameters and constraints (per the below). These time definite/shortened delivery window will result in:
- Improvement in DC workload balancing
- Reduced departure congestion from DC
- Facilitate and improve transportation routing
- Satisfy business constraints required by DC/Store operations; and, compliance with transportation policy and rules and local law
The inputs to the solution approach are:
- Forecasted store case volume, cube and weight data
- Labor hours and time requirements at the DC needed to fulfill forecasted store volumes
- Distances/transit times of DC to store and among stores
The solution was developed to address the following business constraints:
- Plan for each commodity (MP/FDD, DRY)
- Avoid delivery in Noise Ordinance periods. Noise ordinances are regulations that place restrictions on the amount, duration, and source of noise for certain times of the day.
- Avoid delivering to low volume stores during the night. This causes unnecessary deployment of manpower.
- Avoid overlapping of delivery windows (for different commodities) for single dock stores
- DOT (department of transportation) rules
- 30 minutes break after 8 hours of consecutive driving
- A driver may drive up to 11 hours total before he is required to take a 10-hour break.
The risks with this shortened delivery window strategy are an increase in transportation costs due to decrease in number of stores per route (in order to achieve a feasible 4-hour delivery window)
Rapid Implementation required specialized expertise and tools: In order to accelerate implementation, the retailer partnered with a major IT and Business Supply Chain Consulting Firm to evaluate this solution across all DCs.
The engagement included:
- Determining optimized time windows leveraging scientific methodologies and custom algorithms.
- Developing a routing solution that honors these optimized time windows
- Scenario Modeling and Evaluation understanding:
- Cost impact on low/medium and high volume days.
- Cost impact of moving time windows (before/after the noise ordinances).
- Cost impact of addition/reduction of an hour to the delivery time window.
- Visual Review of Results
- DC Metrics: Stockouts at the DC by hour and labor profile
- Transportation metrics: Miles, Drive Time, Wait Time, Number of Trucks, and Duty Time